5x Free Shooting Star Candlestick Patterns PDF Download
- BY pkniftyadmin
- March 15, 2024
- 0 Comments
- 365 Views











Watching investment gains vanish while your held stocks suddenly move backward is becoming intolerable for you. You have probably stayed passive about shorting stocks because you did not know when the prevailing uptrend would give way. Trading professionals consider market reversal recognition as the hardest skill to learn but also one of the most profitable aspects in financial trading. A solitary candlestick pattern exists, which gives developers potential buyers and sellers with superior capabilities to detect bearish trend shifts. Enter the shooting star.
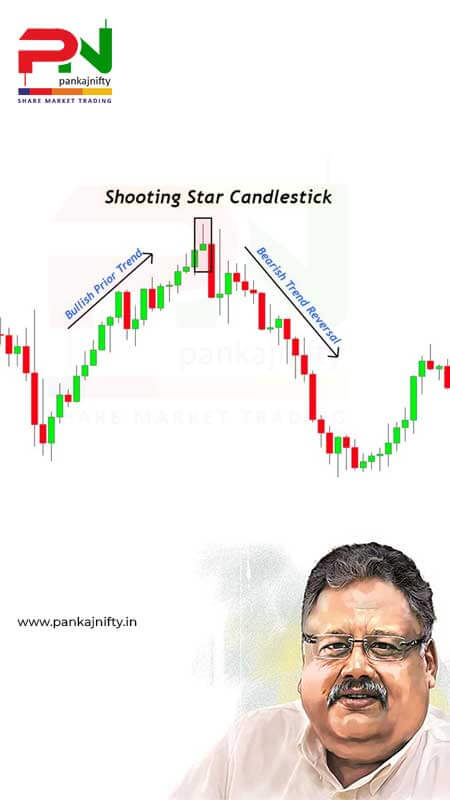
Within uptrend patterns, the visually clear Shooting Star candlestick provides traders with a strong bearish reversal signal. This market indicator reveals changing market forces that shift power from purchasing to selling parties, thus providing professional traders a chance to earn profits through declining price patterns. Both novices and experienced traders use this pattern because of its simple nature together with its high predictive ability provided proper application.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deep into the world of the Shooting Star. You'll learn:
Exactly what a Shooting Star is and the market psychology behind its formation.
How to identify Shooting Star patterns with pinpoint accuracy, avoiding common pitfalls.
Proven trading strategies to capitalize on Shooting Star signals, including entry points, stop-loss placement, and profit targets.
The crucial importance of confirmation and context – factors that separate successful trades from false signals.
Real-world chart examples, both successful and failed, to illustrate the pattern in action.
The limitations of the Shooting Star and how to mitigate risk.
The PDF guide with a cheat sheet is now available free of charge to simplify your understanding of the Shooting Star pattern. The resource provides a full exploration of the pattern to help traders master its application as a tool for their trading system.
What is a Shooting Star Candlestick Pattern?
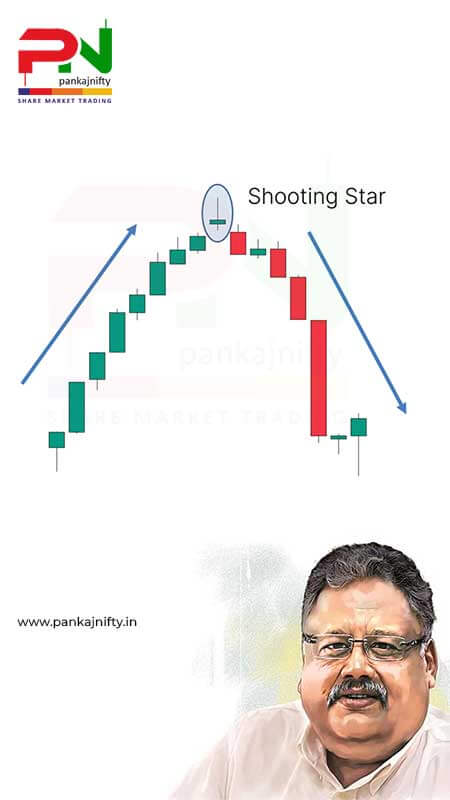
A shooting star stands as a bearish reversal pattern that reveals itself through a single candlestick formation. The rifle-shaped candlestick pattern holds a name that elegantly describes its visual characteristics because it appears similar to the way stars arc through space while trailing a lengthy path. Weights and measurements derived from the trial allow analysts to determine its valuable meaning.
Here's a breakdown of its defining characteristics:
Small Real Body:
A small open and close price distinction exists within a session where the real body sits near the low point of trading activity. Body color that indicates above and below the opening price matters less than the size and position combination. A tiny real body validates that buyers and sellers lacked substantial control at the close time of trading.Long Upper Shadow (Wick):
The most significant indicator emerges from the upper portion of the eclipse (Wick). The real body shadow features an upper component that exceeds the real body length at least two times and extends even longer in an ideal case. A long price shadow indicates the maximum value that buyers attempted to reach while their momentum eventually faded away. This market graph illustrates robust selling power that enters the market.Little to No Lower Shadow:
The price range that buyers initially pushed prices up reveals itself through an extremely short lower shadow or no visible shadow at all. The sellers maintained dominance during the session, which caused the price to stay close to its opening value.Appearance After an Uptrend:
A serious analysis must consider the formation’s appearance during an uptrend period. The reversal pattern of a shooting star works only when it forms following an established uptrend. A shooting star pattern exists only in uptrending markets or trends. Any comparable patterns without an established uptrend should not be traded as Shooters.
The Psychology Behind the Shooting Star:
Learning the nature of pattern formation equals its significance to identifying what the pattern represents. The shooting star presents a tactical competition between buyers and sellers that culminates in the sellers attaining victory.
Here’s the typical scenario:
Uptrend in Progress:
Currently the market demonstrates an uptrend as buyers maintain control to push prices into higher ranges.Initial Bullish Push:
Buyers maintain their control during the first part of the Shooting Star session, thus forcing prices to rise significantly. The long upper shadow develops as a result of this pattern.Sellers Emerge:
During the course of trading, sellers start to push the market price intensively. Multiple factors, such as profit-taking activities, news releases, and changes in market sentiment, affect prices to decrease.Price Reversal:
The price undergoes a reversal when selling pressure defeats buying pressure, thus returning to near its opening level.Close Near the Low:
As the session concludes near the lowest point, the price forms a tiny real body, which produces an extended upper shadow. The market control has transferred from buyers to sellers, which indicates upcoming threats to the previous upward trend.
Distinguishing the Shooting Star from Similar Patterns:
One must distinguish between various candlestick patterns bearing similar features to shooting star patterns while trading. Identifying the wrong pattern instead of the correct one may result in spending money due to trading mistakes.
Hammer:
The Hammer resembles the Shooting Star with its tiny body but long shadow, yet it appears below a downward trend to indicate a bullish reversal signal. Users should evaluate the location of the long shadow below the body.Inverted Hammer:
The Inverted Hammer pattern shows identical features to Shooting Star patterns yet manifests within a downward trend to indicate a bullish change. Prior trend evaluation determines the main distinction between these patterns.Hanging Man:
A Hanging Man shares physical characteristics with the Hammer pattern but forms during uptrend termination where it resembles a Shooting Star, although it displays extended bottom shadows.Doji:
A Doji candlestick reveals indecisiveness because its real body shows low or zero length. The bearish aspect of the shooting star comes from its long upper shadow rather than the doji-like body. A doji by itself is neutral.
How to Identify a Shooting Star Pattern: A Step-by-Step Guide
A successful shooting star recognition goes beyond defining its shape because it demands comprehensive understanding of the situation followed by signal verification. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
Step 1: Identify the Prior Trend – Is it a Clear Uptrend?
A definitive uptrend that precedes it is the condition that makes this pattern valid. A shooting star pattern must form only within a properly established uptrend. A continuous rise in market prices appears as higher highs along with higher lows. A shooting star pattern must not receive interpretation when it forms under conditions of downtrend movement or chaotic market price action.
Look Back: Study the previous price movements that may lead to a shooting star pattern. Have prices been consistently rising?
Trendlines: Students can use trendlines to visually verify the upward price movement.
Moving Averages: The price location above fundamental moving averages, including the 20-day and 50-day moving averages, will signal an uptrend.
Step 2: Look for the Candlestick Shape – Does it Meet the Criteria?
Once you’ve confirmed the uptrend, examine the candlestick itself:
Small Real Body: Is the real body small and located near the low of the session?
Long Upper Shadow: Is the upper shadow at least twice the length of the real body? The longer, the better.
Little/No Lower Shadow: Is the lower shadow minimal or absent?
Step 3: Consider the Context – Is the Signal Strong?
A Shooting Star by itself does not provide certain evidence about selling opportunities. A Shooting Star’s reliability depends heavily on the factors existing in the market area.
Volume: The ideal conditions for the shooting star to form include high market volume levels. The appearance of numerous sellers in the market provides enough weight to validate the reversal signal according to this data. Check that the volume during the Shooting Star shows a substantial increase from the previous candles.
Resistance Levels: The formation of a shooting star should occur close to established resistance points. The areas where sellers previously intervened to stop price increases become resistant price zones. Common resistance levels include:
Previous Highs: Prior swing highs where the price reversed.
Trendlines: Downward-sloping trendlines connecting previous highs.
Fibonacci Retracement Levels: Key levels (e.g., 38.2%, 50%, 61.8%) derived from the Fibonacci sequence, often act as support and resistance.
Moving Averages: Major moving averages (e.g., the 200-day moving average) can act as dynamic resistance.
Psychological Levels: Round numbers (e.g., $50, $100) often act as resistance.
A Shooting Star forming at a resistance level significantly increases its probability of success.
Overall Market Conditions: Extra market data indicators which show signs of decline in the S&P 500 index or equivalent benchmark for stock markets help predict the success of this reversal pattern. A secondary bearish market trend enhances the chances of executing a profitable Shooting Star price reversal pattern. Strong upward market trends tend to overcome the detection of shooting star patterns.
Confirmation: This is crucial. When using the Shooting Star pattern only for making trading decisions, consider doing so carefully. Confirm that a bearish reversal is actually starting before proceeding. A close below the shooting star low on the following candle(s) represents the main method to confirm this pattern. Other forms of confirmation include:
A bearish engulfing pattern following the Shooting Star.
A breakdown below a support level.
A gap down below the Shooting Star’s low.
Step 4: Avoid Common Mistakes – Don't Fall for These Traps!
Even experienced traders can make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid:
Ignoring the Prior Trend: This is the biggest mistake. A Shooting Star must appear after an uptrend.
Trading Without Confirmation: Jumping into a trade too early, before the reversal is confirmed, can lead to losses.
Misinterpreting Similar Patterns: Don’t confuse a Shooting Star with a Hammer, Inverted Hammer, or Hanging man.
Ignoring Volume and Context: Volume and resistance levels significantly impact the reliability of the signal.
Not Using a Stop-Loss: Always, always use a stop-loss to protect your capital.
Trading the Shooting Star Pattern: Strategies for Success
Trading plan development becomes necessary after validating the shooting star formation and its associated signal. The following strategies exist to suit different risk appetites, starting from aggressive through to conservative:
Entry Points:
Aggressive Entry: Begin a short position immediately after a Shooting Star closes or select put options for purchase at that moment. The highest potential reward accompanies this strategy, although the highest risk exists since confirmation of the reversal might fail.
Conservative Entry (Recommended): Enter the market only after receiving confirmation signals from the pattern (recommended approach). The main confirmation method requires the following candle to close lower than the shooting star’s lowest point. Implementing this strategy reduces the likelihood of wrong trading signals, yet it may cause you to delay your position entry during the price decrease.
Break of support entry: The entry requires waiting until a specific support threshold breaks away.
Stop-Loss Placement:
A stop-loss is essential for managing risk. It’s a predetermined price level at which you’ll exit the trade if it moves against you.
Above the High of the Shooting Star: Using stopping power at the high point of the shooting star remains a standard and rational approach to placing stops. The bearish signal from the shooting star becomes invalid when the price rises above its initial high.
Above a Resistance Level: Placing a stop-loss above a strong resistance level should be done along with a proper position when the Shooting Star pattern appears in that area.
Profit Targets:
Setting a profit target helps you lock in gains and avoid holding a position for too long.
Support Levels: You should check for potential support levels to function as profit targets. Prior periods where buyers entered the market have created these areas, which served to prevent price declines. Common support levels include:
Previous Lows: Prior swing lows where the price reversed.
Trendlines: Upward-sloping trendlines connecting previous lows.
Fibonacci Retracement Levels.
Moving Averages.
Psychological Levels.
Measured Move: A basic approach to finding trading metrics involves measuring Shooting Star height then extending the distance achieved downward from its lowest point. The distance from high to low measurement functions as a potential price target.
Risk/Reward Ratio: Among trading positions, always maintain a ratio that benefits rewards over risks. Your anticipated profit should remain substantially larger than the projected loss amount. A standard objective when performing risk management is to establish a ratio of 1:2 or 1:3 that matches rewards against risks. Risk $1 per share, and your target profit should exceed $2 or $3 per share.
Risk Management – Protecting Your Capital:
Always Use a Stop-Loss: This is non-negotiable. It’s your safety net.
Manage Position Size: Don’t risk too much of your capital on a single trade. A general rule of thumb is to risk no more than 1-2% of your trading account on any one trade.
Be Aware of Market Conditions: Consider the overall market trend and any relevant news events that could impact your trade.
Don’t Chase Losses: If a trade goes against you, accept the loss and move on. Don’t try to “make it back” by increasing your position size or taking on more risk.
Use a Demo Account: Before trading with real money, practice identifying and trading Shooting Star patterns in a demo account. This allows you to gain experience without risking your capital.
Limitations of the Shooting Star Pattern
No technical indicator is perfect, and the Shooting Star is no exception. It’s important to be aware of its limitations:
False Signals: The chart pattern of shooting stars induces erroneous signals mostly when market conditions remain volatile or stagnant. Confirmation plays a vital role because of how important this pattern structure proves to be.
Not a Standalone Indicator: Technicians should use shooting stars solely as part of a complete analysis framework alongside additional technical indicators such as volume and trend-related elements.
Market Context is King: The current market trend, together with important market events, can permanently shift the reading of a shooting star pattern. A healthy uptrend in the market makes it likely for bearish reversal patterns to disappear.
Subjectivity: Subjective considerations may arise when either establishing the preceding trend definition or correctly interpreting if a candlestick conforms to shooting star standards.
Free PDF Download: Your Shooting Star Mastery Guide
Your understanding of the shooting star requires more depth according to what we have developed. A free PDF summary document encompasses all the information from this article together with expanded material:
Detailed Explanation: A complete breakdown of the Shooting Star pattern, its characteristics, and its psychology.
Identification Checklist: A step-by-step checklist to help you quickly and accurately identify valid Shooting Stars.
Trading Strategies: Detailed trading strategies, including entry points, stop-loss placement, and profit targets.
Risk Management Tips: Essential guidelines for protecting your capital and minimizing losses.
Real-World Examples: Additional chart examples to reinforce your understanding.
Printable Cheat Sheet: A handy, one-page cheat sheet that you can print out and keep by your trading station for quick reference.
This PDF is your ultimate resource for mastering the Shooting Star. It’s designed to be practical, actionable, and easy to use. Don’t miss out on this valuable opportunity to enhance your trading skills!
Final Thoughts: Getting the Hang of the Shooting Star for Reliable Earnings
Candlestick pattern Shooting Star stands as an effective indicator that helps traders detect bearish market changes. Using this pattern correctly leads to a substantial enhancement of your trading outcomes. Similar to other technical indicators, the shooting star pattern carries its limitations. Success requires:
Thorough Understanding: Knowing the pattern’s characteristics, psychology, and limitations.
Accurate Identification: Following the step-by-step identification process and avoiding common mistakes.
Confirmation and Context: Waiting for confirmation and considering volume, resistance levels, and overall market conditions.
Sound Risk Management: Always using stop-losses, managing position size, and being aware of potential risks.
Practice: The more you practice identifying and trading Shooting Stars (in a demo account first), the better you’ll become.
Keep in mind that the shooting star functions as only one analytical instrument for trading. Implement the Shooting Star pattern with trading tools from technical analysis and fundamental analysis and a structured trading plan to increase your trading success.
Your FREE PDF guide can be downloaded now to help you detect those important reversals. By obtaining our available knowledge and resources, we are certain you will take your trading skills to a higher level of profitability.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Trading involves risk, and you could lose money. Always do your own research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any trading decisions. Past performance is not indicative of future results.